[vc_row el_class=”cstm_container”][vc_column][vc_column_text]Body joints have a complicated makeup, due to which they are prone to suffering from a large number of ailments. One such health condition that causes discomfort and pain along the joints is bursitis, caused by inflammation of the bursa.
What is bursa?
During joint movement, tendons, ligaments, muscles,s and skin glide over bones. This gliding motion is supported by small fluid-filled, slippery sacks known as bursae (plural of bursa). Wedged between bone and soft tissue and acting as a cushion, bursae eliminate the possibility of friction during joint movement.
What is bursitis?
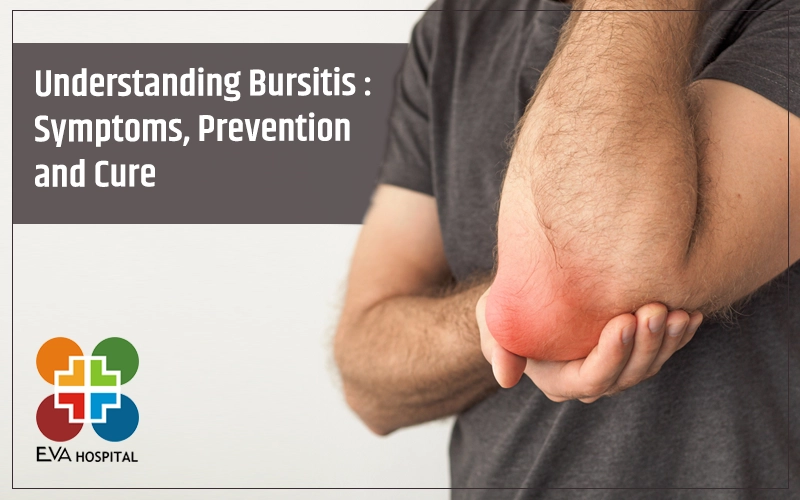
Any inflammation or irritation in these miniature water balloons — a human body has as many as 140 of them— is known as bursitis. The prepatellar bursa, which is one of the biggest bursae in the body, is only 3 mm thick. Typically a temporary condition, bursitis can only limit motion for the time it lasts and seldom causes any deformity.
Common areas affected by Bursitis
Bursitis can affect any joint that goes through excess repetitive action. Your shoulder, elbow, and hip and the three most vulnerable areas to Bursitis. While not that common, this condition can also affect your knee, heel, and the base of the big toe. Some of the common types of bursitis include:
- Retromalleolar tendon bursitis
- Posterior Achilles tendon bursitis
- Hip bursitis
- Elbow bursitis
- Knee bursitis
- Kneecap bursitis
Bursitis symptoms
- Swelling
- Inflammation
- Pain
- Discomfort during movement
Since there is a great deal of overlap in the symptoms caused by bursitis and other joint-related ailments, it is always advisable to visit a medical practitioner to detect this condition. Your doctor can ascertain the cause of these symptoms with a physical examination, blood tests, MRI, ultrasounds, and X-rays, etc.
Bursitis: Risk factors
Age: Elderly are at higher risk.
Profession: Those engaged in professions that require extensive kneeling on their elbows. These may include tile setting, gardening, painting, and playing musical instruments or carpet laying are prone to developing Bursitis.
Medical condition: People with weight issues, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and diabetes are at higher risk of developing Bursitis.
Bursitis: Treatment
Typically, rest, anti-pain medication, and icing will help treat the condition. In chronic and severe cases, surgery may be required to remove the infected bursae. Early detection and treatment of this condition are of utmost importance because untreated bursitis has the tendency to turn chronic.
Bursitis prevention tips
- Warm-up exercises
- Yoga
- Breaks during work
- Weight loss
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]