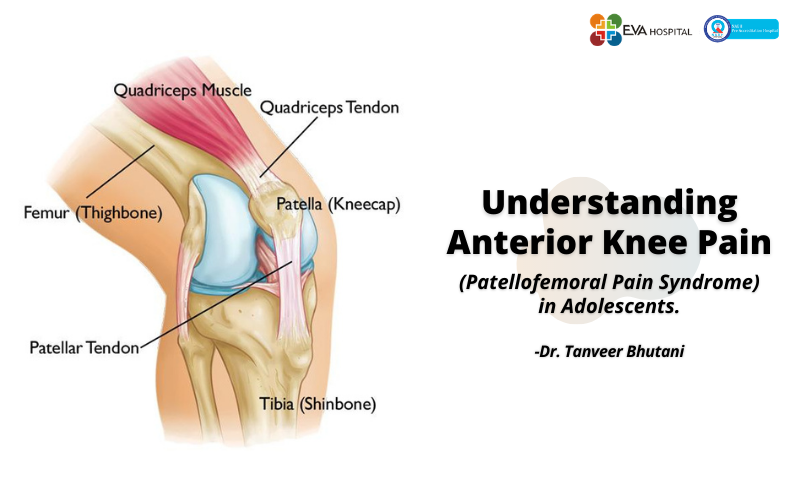
Understanding Anterior Knee Pain (Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome) in Adolescents.
 All Blogs
All Blogs
Understanding Anterior Knee Pain (Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome) in Adolescents.
Anterior knee pain in adolescents is a trauma that is localized in the front and center of the knee, right above the shin bone, below the knee cap.
AKP is sometimes also called PF syndrome (PFS), or chondromalacia patellae. Commonly, it is referred to as “runner’s knee,”
Teenagers or young adults who take part in sports commonly experience this condition, especially females.
It is a common complaint diagnosed as such when all other conditions are ruled out.
Symptoms
The outset of the Anterior knee pain is gradual, though in rare cases, a sudden trauma may occur. The most predominant symptom is a vague discomfort around the kneecap or behind it.
The patient usually finds it hard to pinpoint the exact origin of the pain.
Other common symptoms include clicking noise, reduced knee flexion, and occasional giving-way of the joint.
Causes
Adolescent anterior knee pain has a broad and differential diagnosis. generally speaking, we might say that it occurs due to overuse or not backing up sports with sufficient strengthening and warming up exercises.
However, there can be multiple other causes to trigger this condition, namely:
- Rigid or weak quadriceps and hamstrings.
- Imbalance of thigh muscles that hold the knee joint
- Unbalanced legs shape so that the kneecap or patella is out of alignment.
- Undergoing inappropriate sports training methods or equipment
- Issues caused by using new footwear or playing surface. There may be inflammation caused thus, around the joint.
- Overuse of a set of muscles in performing sports workouts. Or, alterations in training causing stress on the tendons and bones in the frontal knee.
- Referred pain from a problem in the hip or femur. Hips and the thigh bones should be carefully examined.
- Osteochondritis dissecans-Cartilage defect in the knee joint.
- Inflamed ligaments and tissues surrounding the knee.
- Bony tumor – it is very uncommon and benign, but must be ruled out.
- History of prior injury, surgery, or joint disease
Treatment
Anterior knee pain is a common complaint but can be a concern for children and their families. It is rarely caused by a serious medical condition. Once, diagnosed, the treatment largely depends on the causes.
Investigations may include an x-ray and MRI( magnetic resonance imaging) to determine the cause. MRI allows a more detailed evaluation of soft tissues, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage.
Clinically, your orthopedic surgeon would test the strength, flexibility as well as range of movement.
To control swelling and inflammation, ice packs and none steroid anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs are prescribed. A rest from pain-inducing activities is required.
For overuse injuries, once the pain subsides, a modification in the athletic activities and training techniques is essential.
In most cases, a stretching and strengthening program designed by a physical expert can curtail the adolescent’s AKP. A knee guard or sleeve is also helpful in providing relief from the trauma.
Rehabilitation
To keep the anterior knee pain under control for your adolescents, especially when they are active in sports, you must adhere to a joint-friendly program.
The athletic training should be prescribed by your doctor. Workouts must include exercises that strengthen the hamstrings and quadriceps, making them flexible.
Movements that trigger pain should be curtailed.
Footwear must be carefully chosen based on the sport or activity the youngster is indulging in. There are specific shoes for jogging, tennis, football and all other games.
And of course, the child must wear shots.
The playing surface has a role to play too. If there has been a sudden shift in the ground type in the past, it should be contemplated in the future too.
Clay, concrete, wooden, and grass- different grounds impact the knees differently according to their buffering ability.
Instead of stopping everything, alternative sports such as cycling and walking should be encouraged.
Over a period of a few weeks, the child can return to normal sporting activities.
Conclusion
Anterior knee pain is prevalent in children and adolescents. Diagnosis is challenging & mandates a detailed history and physical examination.
Common causes involve the patellofemoral joint and the extensor mechanism of the knee.
It is important to rule out conditions of systemic diseases such as inflammatory conditions and malignancy.
A thorough study of the patient’s history and clinical exam leads to the correct diagnosis and treatment of PFP.